Some people being treated with alpha1 adrenergic blocking drugs such as Tamsulosin, Prazosin, Alfuzocine, Terazosin and Doxazocine, a complication may occur during cataract surgery, which we know in Ophthalmology as Flaccid Iris Syndrome or IFIS.
These drugs are commonly used to control urination symptoms in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia or enlargement of this gland, and also, to control systemic blood pressure.
The most used today is Tamsulosin, and in patients with this treatment in a chronic way , it is very common to find this syndrome so annoying when they have surgery.
Adrenergic alpha 1 blockers inhibit prostate gland receptors, thus preventing their enlargement, but at the same time, they attack and bind to pupil dilator muscle receptors. This causes a characteristic triad that we already observe in the presurgical exploration.
1.- Poor pupillary dilation when administering the usual drugs for it by instillation.
2.- Introsurgical myosis (very small pupil).
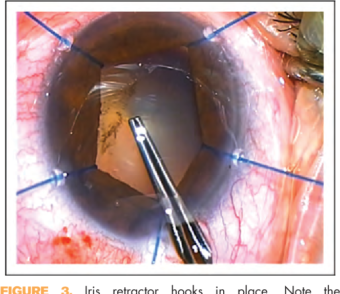
3.- Flaccidity of the iris, this means that at different stages of the surgery, a hernia is produced through the incisions and is continuously toneless. That makes all the surgical steps that have been taken quite difficult and, in addition, can greatly increase complications.
Before knowing the cause of this syndrome and its symptoms, we saw surgeries in which there was iris rupture, zonular disintegrations, hemorrhages in the anterior chamber or hyphemas, and patients presenting with post-surgical ocular tension peaks, as well as double vision or diplopia and greater discomfort with light due to damage to the iris (photophobia).
In the interview to the patients before being operated (anamnesis), we place a lot of emphasis talking about the drugs that affect blood clotting and platelet aggregation, as well as the intake of alpha 1 adrenergic blocking drugs.
This means that ophthalmologist surgeons, when we have surgeries, are prepared with an arsenal of measures that minimize possible complications.
For this surgery preparation, we use high molecular weight intraocular gels, which better stabilize the pupil, we use intracamerular Atropine or Phenylephrine to achieve a better mydriasis or iris dilation, and we have the iris expanders that are hooks or special rings that mechanically hold the pupil with the least number of possible complications.
The effect that these drugs produce on the iris is chronic and has a memory effect. This means that the iridian atrophy and weight loss they cause does not improve even if they are suspended one month before surgery. In addition, the consequent deterioration in the quality of life of patients with prostatism, which needs to go to the toilet several times during the night.
There are currently no scientific studies that can prove that suspending these treatments until one month before surgery significantly reduces the risk of suffering from IFIS.
And we also have to say that not all patients who take them end up suffering from IFIS.
Whenever we suspect that a patient may have this syndrome, we explain it, we notify the patient of the possible connotations that he may have regarding this matter, and that is why we are prepared with our surgical preventive measures.
The increase in life expectancy has made the use of these medicines more prolific for patients with prostate problems because this symptomatology is closely related to old age.
Eye Clinic Dra.Carreter

Recent Comments