One of the subspecialties within the field of Ophthalmology is oculoplastic surgery. This specialty consists of the diagnosis and treatment of the different pathologies that affect the structures that surround the eye. These are the ocular appendages such as the eyelids, the lacrimal ducts, the lacrimal gland and the orbit.
There is a wide range of pathologies such as surgical techniques, but we are going to describe those that we usually find in our medical consultation and are more common in most cases.
1.- BLEPHAROPLASTY
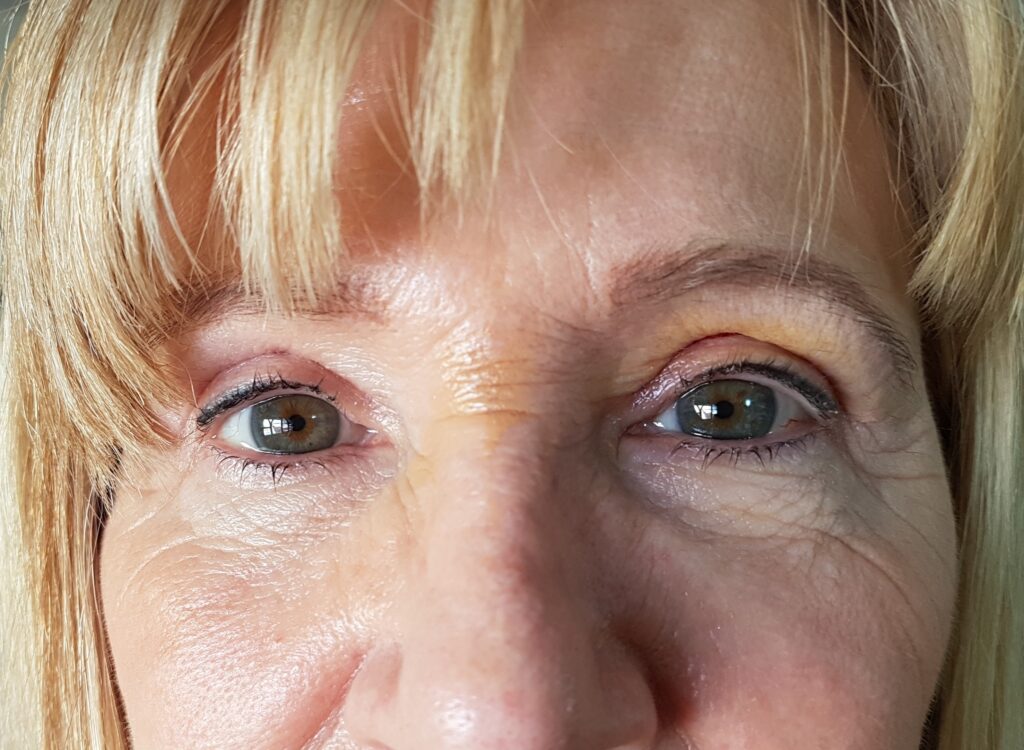
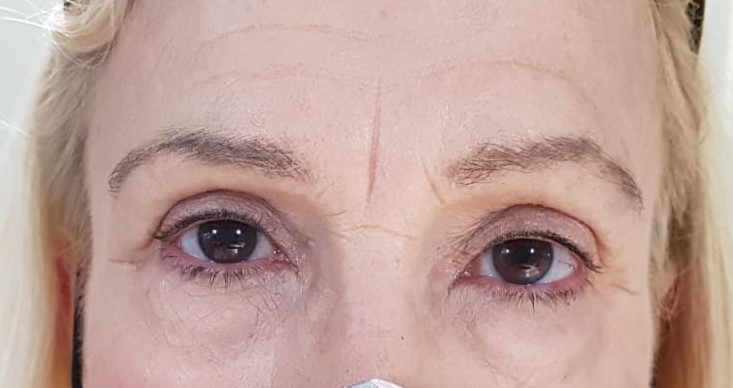
These are surgical techniques that help aesthetically to improve the tired appearance of the eyes due to the passage of time and to rejuvenate the look on the face. Age and years and also genetic factors, produce a redundancy of the skin of the eyelids, as well as a bulge of the periocular fat bags by relaxation of the orbital septum. All this produces a more aged appearance. That is why this surgical technique is the one that removes excess skin and fat on the lower, upper eyelids or both.
The way to perform an upper blepharoplasty is by accessing the skin, leaving the scar completely hidden by the mobile skin wrinkle of the upper eyelid.
For surgery of the lower eyelids, it can be done with the transconjunctival technique and not scar or through the anterior approach.
In many cases, it is also necessary to fix or anchor the outer edge or outer edge of the lower eyelid to the outer periosteum in order to keep it in the correct position and thus avoid residual ectropion (eyelid everted out).
However, although these techniques greatly improve the aesthetic aspect, they have limitations. It is very important to treat the eyelid well, but allowing the eyelid to continue performing its ocular protective function. The correct functionality of the eyelid is crucial to avoid possible complications in the future.
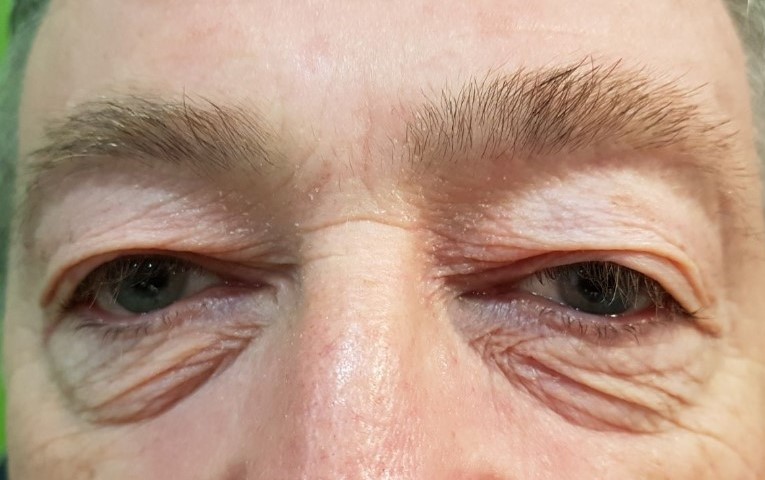
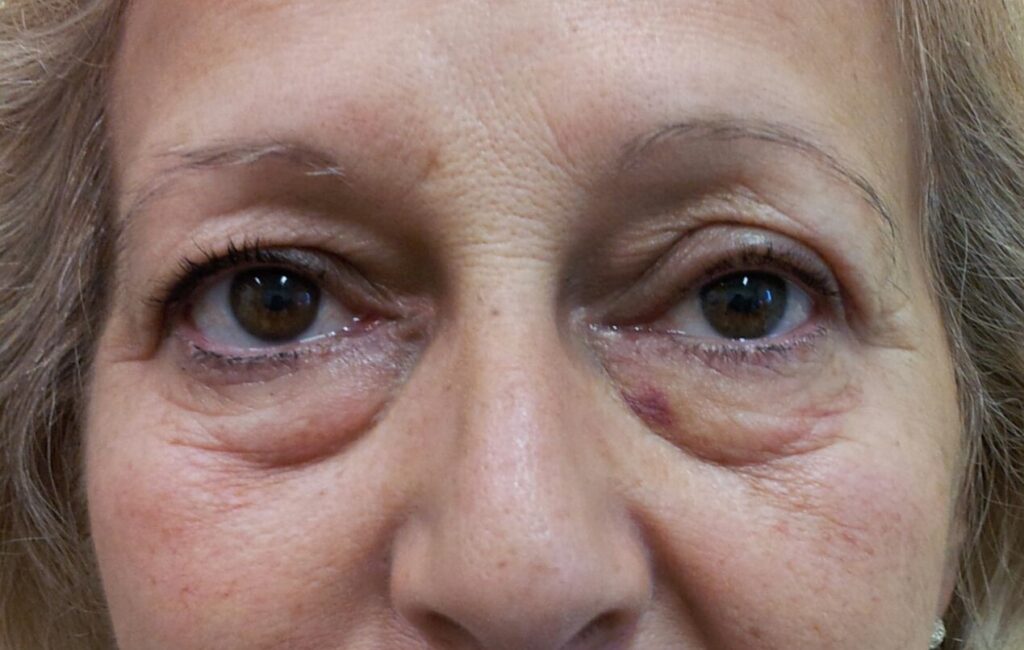
1.- This patient has significant excess skin on the upper and lower eyelids. Complete blepharoplasty was performed with fixation of the outer edge to the periosteum. See photo before and after.
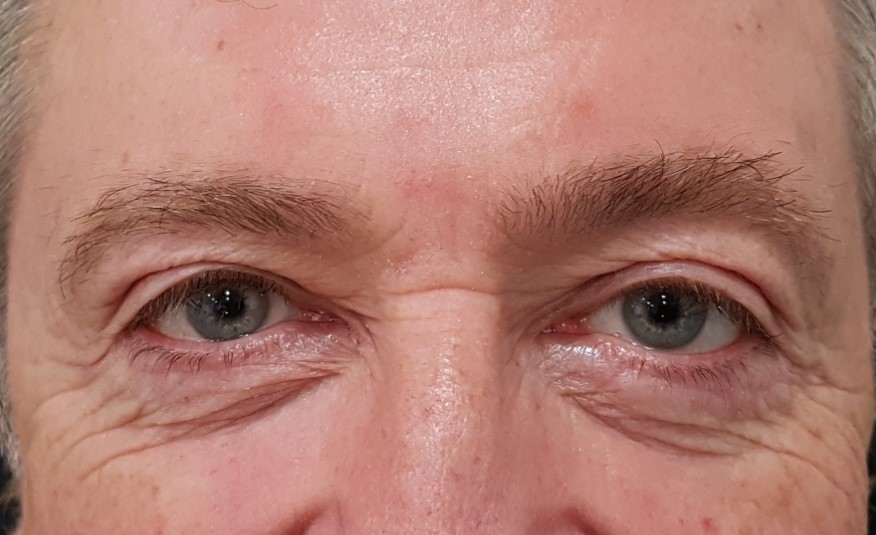
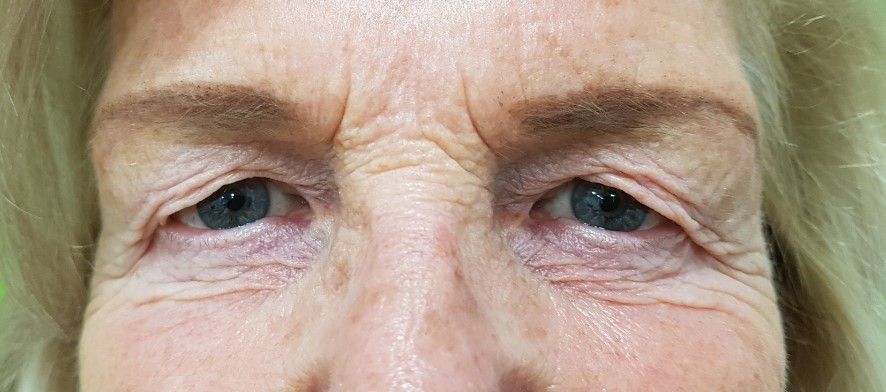
2.-Patient with heavy upper eyelid appearance before surgery.This aspect has desappeared a month after upper blepharoplasty.
3.-Upper Blepharoplasty before and after.
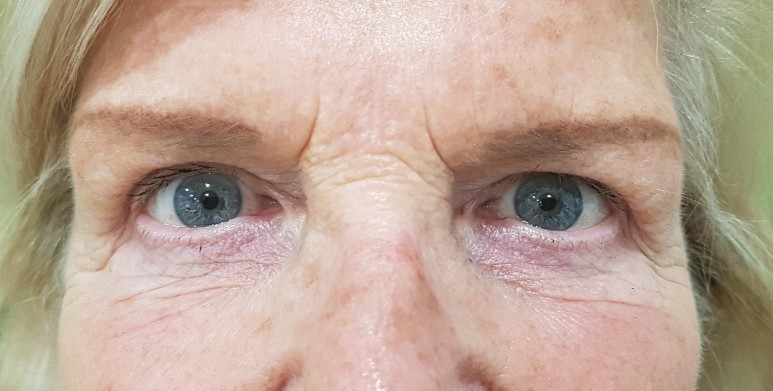
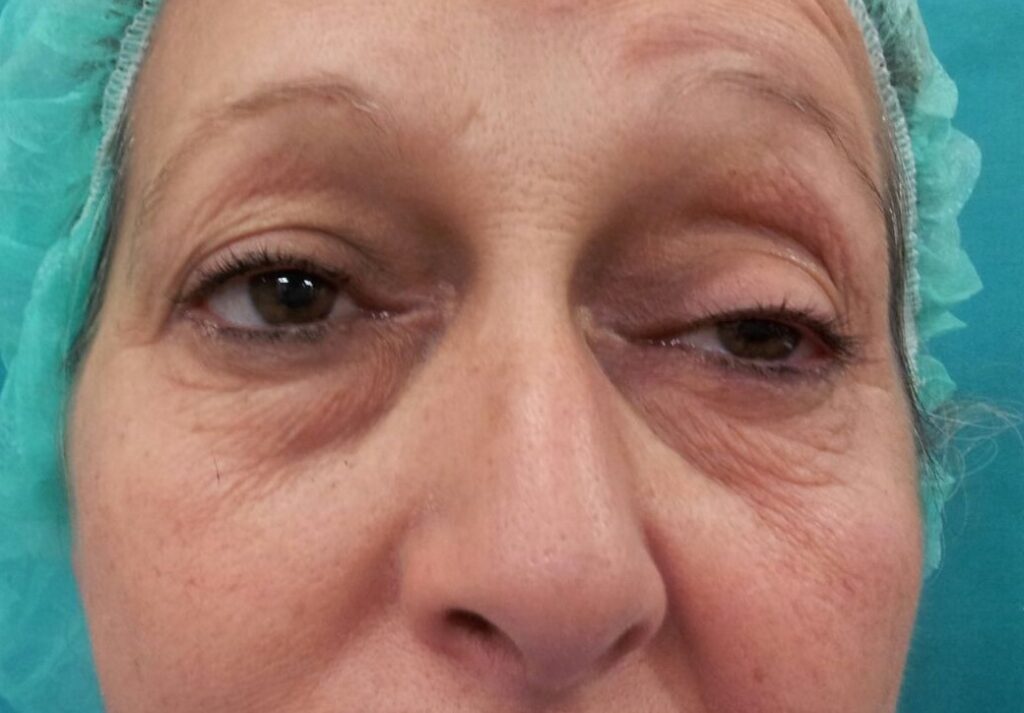
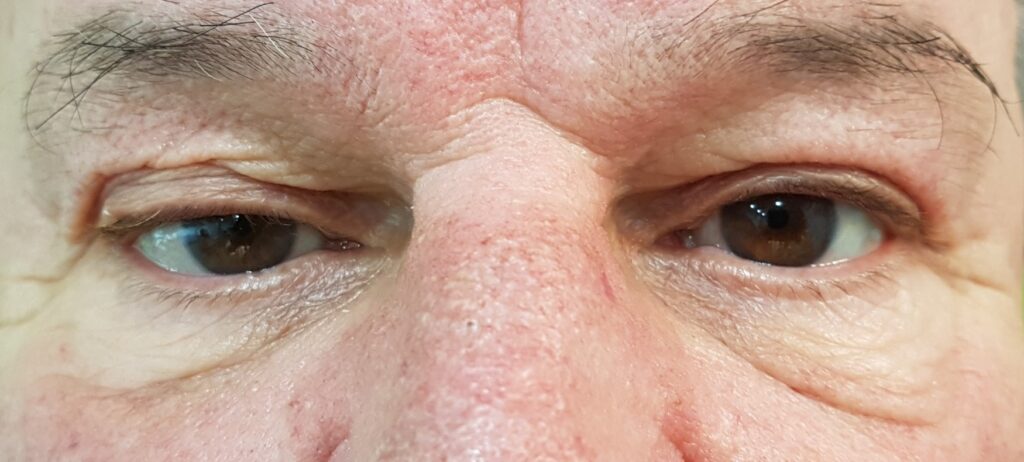
4.- Patient has asymmetry of the upper eyelids due to previous surgery in adolescence. Only the upper right eyelid was operated on, eliminating the central fat packet and leaving the medial one to seek symmetry.
The result was excellent.
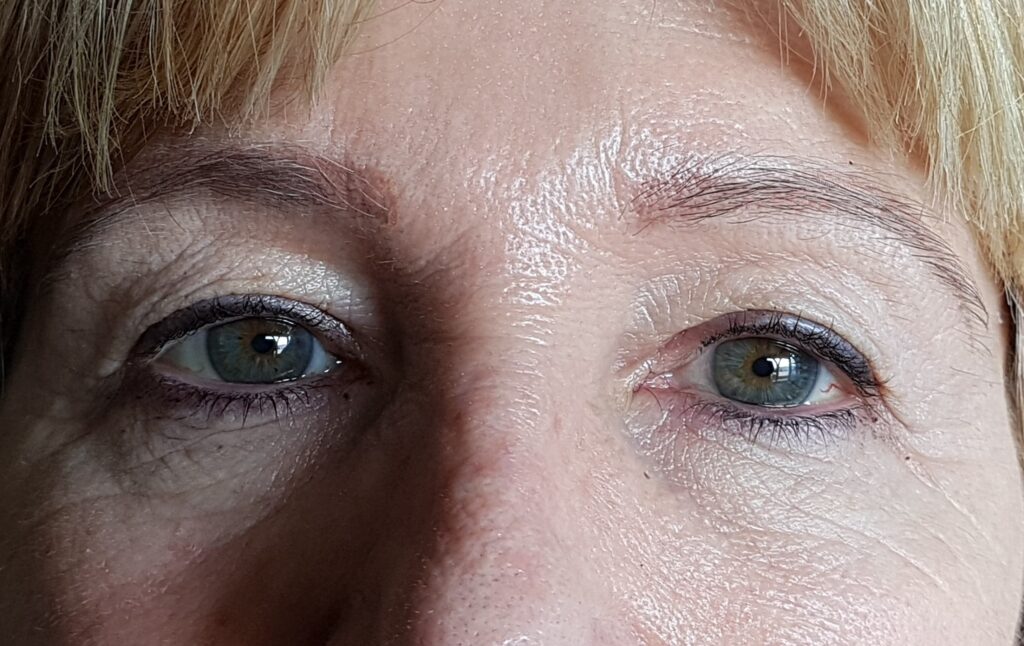
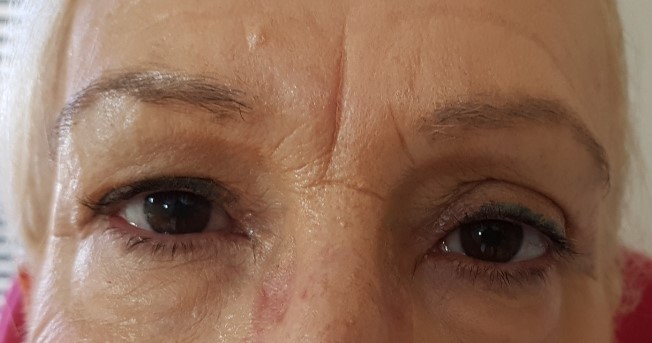
5.-In this patient, excess skin and associated xanthelasmas were removed at the same time. Before and after photos.
PALPEBRAL PTOSIS
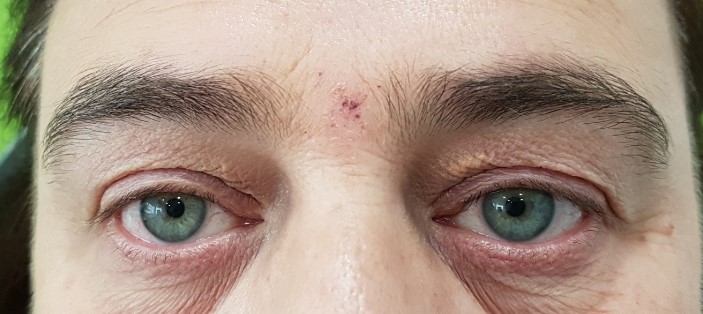
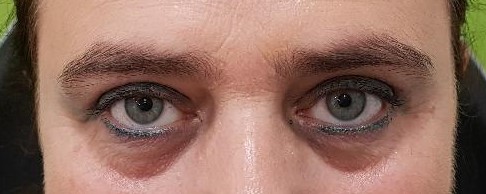
Eyelid ptosis is when the edge of the upper and / or lower eyelid falls from its original position.
When the upper eyelid is affected (usually in advanced age), it is due to a dehiscence of the levator muscle of the upper eyelid. This effect can also occur in a common rubs for allergic conjunctivitis.
Some patients even have their vision affected because it can cover the visual axis. For this reason many of them are forced to make involuntary contractions of the forehead or neck in order to raise the eyebow and leave the visual axis free to see.
There are several anterior and posterior approach techniques, but the most used are Mullerectomy and resection and reinsertion of the levator eyelid muscle.
The first technique is performed posteriorly and in mild ptosis of up to 2 mm, having the advantage of the absence of scar and a skin wrinkle after surgery with the same appearance and height as the contralateral eye.
The second technique is an anterior approach, it can be associated with blepharoplasty and has the disadvantage of the difficulty in adjusting the skin wrinkle in height and shape.The great advantage is that it corrects more sever ptosis.
Congenital ptosis are those that appear in patients from birth, they are surgically intervened in order to avoid amblyopia or lazy eye. The fixation of the levator muscle to the frontal muscle has been the technique most used and lately the flap of the frontal muscle anchored, doing a pulley, to the superior tarsus has given very good results.
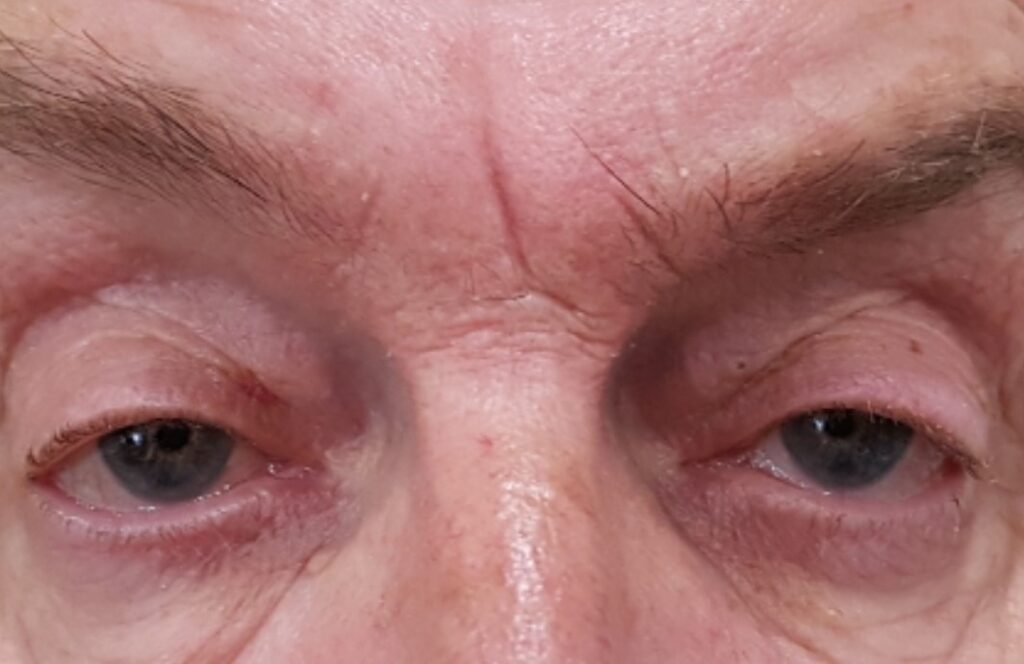
6.- Left upper eyelid ptosis corrected with resection of the left levator muscle and tarsal anchorage.
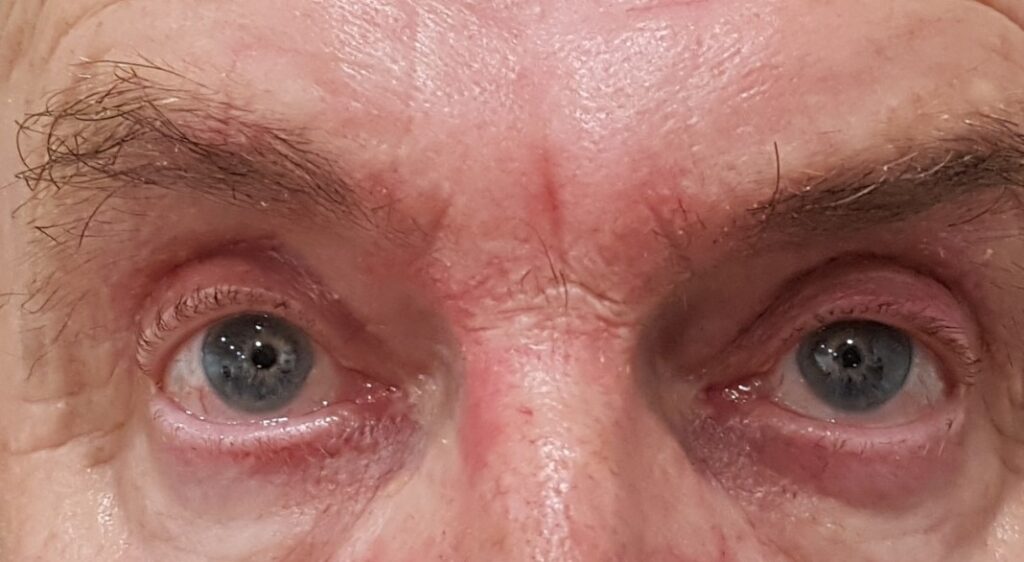
7.- Severe bilateral ptosis hindering the vision of the patient. Before and after surgery. Asymmetry due to upper right ptosis.
8.- This patient underwent surgery for the same eyelid years ago. Blepharoplasty is associated and symmetry is achieved. Photo before and after.

Recent Comments